Product Manager:Nick Wilde


Hydrogen peroxide urea adduct (UHP) is a non-toxic, odorless crystalline solid that contains 35% hydrogen peroxide and releases it upon application.
Recent Literature
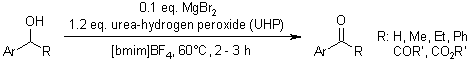
Hydrogen peroxide urea adduct (UHP), when combined with a catalytic amount of magnesium bromide, effectively oxidizes primary and secondary benzylic alcohols to their corresponding aromatic aldehydes and ketones.
H. J. Park, J. C. Lee, Synlett, 2009, 79-80.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1087391

Methyltrioxorhenium (MTO) catalyzes the oxidation of methyl trimethylsilyl ketene acetals using hydrogen peroxide urea adduct (UHP), yielding α-hydroxy and α-siloxy esters. Subsequent treatment with potassium fluoride provides the α-hydroxy esters in high yields.
S. Stanković, J. H. Espenson, J. Org. Chem., 2000, 65, 5528-5530.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jo000212e
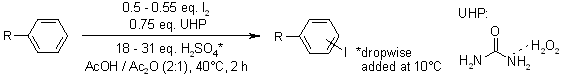
Environmentally benign laboratory methods enable the oxidative iodination of diverse activated and deactivated arenes using molecular iodine, with UHP (percarbamide)—a stable, strongly hydrogen-bonded solid urea-hydrogen peroxide adduct—serving as the oxidant.
P. Lulinski, A. Kryska, M. Sosnowski, L. Skulski, Synthesis, 2004, 441-445.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-815955

The hydrogen peroxide urea adduct (UHP) is a stable, cost-effective, and user-friendly reagent. It serves as an efficient solid-phase oxidant for diverse organic transformations, including:
R. S. Varma, K. P. Naicker, Org. Lett., 1999, 1, 189-191.
https://doi.org/10.1021/ol990522n

The combination of 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) and hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) facilitates a simple and high-yielding synthesis of N,N-disubstituted formamides from imines through an oxidation-rearrangement process under mild reaction conditions.
N. Llopis, P. Gisbert, A. Baeza, J. Org. Chem., 2020, 85, 11072-11079.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.0c01579
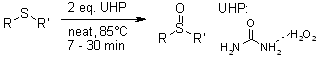
Hydrogen peroxide urea adduct (UHP) is a stable, inexpensive, and easily handled reagent. UHP is used for efficient solid-state oxidation of various organic compounds, including: hydroxylated aldehydes and ketones (converted to hydroxylated phenols), sulfides (oxidized to sulfoxides and sulfones), nitriles (transformed to amides), and nitrogen heterocycles (yielding N-oxides).
R. S. Varma, K. P. Naicker, Org. Lett., 1999, 1, 189-191.
https://doi.org/10.1021/ol990522n
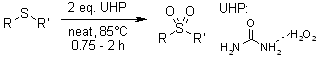
Hydrogen peroxide urea adduct (UHP) represents a stable, cost-effective, and operationally simple oxidizing agent. This compound demonstrates remarkable efficacy in solid-phase oxidative transformations of diverse organic substrates, specifically enabling: the conversion of hydroxylated aldehydes and ketones to hydroxylated phenols, the oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides and sulfones, the transformation of nitriles to amides, and the oxygenation of nitrogen heterocycles to N-oxides.
R. S. Varma, K. P. Naicker, Org. Lett., 1999, 1, 189-191.
https://doi.org/10.1021/ol990522n
The combination of hydrogen peroxide urea adduct (UHP) and phthalic anhydride in ethyl acetate provides a metal-free, eco-friendly oxidation system that selectively converts substituted sulfides to sulfones, with no detectable formation of sulfoxide intermediates.
M. Lutz, M. Wenzler, I. Likthotvorik, Synthesis, 2018, 50, 2231-2234.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1609446
Employing hydrogen peroxide urea adduct (UHP) as the terminal oxidant with diphenyl diselenide as the catalyst facilitates a highly selective catalytic oxidation process that converts sulfides to their corresponding sulfoxides.
P. C. B. Page, B. R. Buckley, C. Elliott, Y. Chan, N. Dreyfus, F. Marken, Synlett, 2016, 27, 80-82.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1378827
Hydrogen peroxide urea adduct (UHP) is a stable, cost-effective, and user-friendly chemical reagent. This compound serves as an efficient oxidant for solid-phase transformations of various organic substrates, including: conversion of hydroxylated aldehydes/ketones to phenolic derivatives, oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxide/sulfone products, transformation of nitriles into amides, and oxygenation of nitrogen-containing heterocycles to N-oxide compounds.
R. S. Varma, K. P. Naicker, Org. Lett., 1999, 1, 189-191
https://doi.org/10.1021/ol990522n
We report a versatile, high-yielding, and eco-friendly catalytic oxidation method for the chemoselective conversion of imines to nitrones, featuring excellent operational simplicity and environmental compatibility.
G. Soldaini, F. Cardona, A. Goti, Org. Lett., 2007, 9, 473-476.
https://doi.org/10.1021/ol062862w
An improved protocol enables the direct synthesis of hypervalent [bis(trifluoroacetoxy)iodo]arenes while eliminating hazardous reagents, requiring only aqueous extraction for workup.
T. Keri Page, T. Wirth, Synthesis, 2006, 3080-3084.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-942543
Quoted from:https://www.organic-chemistry.org/chemicals/oxidations/hydrogenperoxide-urea-adduct.shtm
Aladdin:https://www.aladdinsci.com





