Plant tissue water content is an important indicator of plant water status. Plant tissue water content not only directly affects plant growth, stomatal condition, photosynthesis, and even crop yield, but also plays a crucial role in the quality of fruits and vegetables and the safe storage of seeds and grains. Therefore, learning to measure plant tissue water content is of great significance in the study of plant water physiology.
Principle
The basic principle of the determination of the water content of plant tissues is to use the principle that water can evaporate into water vapor when it meets heat, and the water content of plant tissues can be determined by heating and drying method. There are two ways to express the water content of tissues: one is to express it on the basis of fresh weight; the other is to express it on the basis of dry weight. Sometimes it is also expressed as relative water content (RWC, or saturated water content), which is more indicative of its physiological significance.
Fresh weight and dry weight methods:

Where: Wf - Tissue fresh weight;
Wd-Tissue dry weight.
Relative water content (RWC) of plant tissue refers to the percentage of tissue water content to saturation water content:
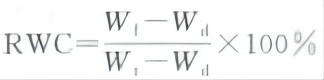
Where: Wt a weight of tissue fully saturated by water.
Water saturation loss (WSD) refers to the size of the difference between the actual relative water content of the plant tissue and the saturated relative water content (100%). It is often expressed by the following formula:
WSD = 1 - RWC
For actual measurement, the following formula can be used:
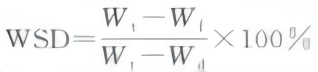
Relative water content and water saturation deficit can be used as indicators for comparing the water retention capacity of plants and for extrapolating the degree of water requirement. The water saturation deficit when the water content of plant tissues is reduced to the point where it produces irreversible permanent damage is called the critical saturation deficit.
Operation method
Determination of water content of plant tissues
Principle
The basic principle of the determination of the water content of plant tissues is to use the principle that water can evaporate into water vapor when it meets heat, and the water content of plant tissues can be determined by heating and drying method. There are two ways to express the water content of tissues: one is to express it on the basis of fresh weight; the other is to express it on the basis of dry weight. Sometimes it is also expressed as relative water content (RWC, or saturated water content), which is more indicative of its physiological significance. Fresh weight method and dry weight method: where: Wf - tissue fresh weight; Wd - tissue dry weight. Relative water content (RWC) of plant tissues refers to the percentage of saturated water content of tissues: where: Wt - weight of tissue fully saturated with water. Water saturation loss (WSD) refers to the size of the difference between the actual relative water content of plant tissue and the saturated relative water content (100%). Commonly used in the following formula: WSD = 1 - RWC actual measurement, can be calculated in the following formula: relative water content and water saturation loss can be used as a comparison of the plant's water retention capacity and deduce the degree of water demand indicators. The water saturation loss when the water content of plant tissues is reduced to the point where permanent irreversible damage occurs is called the critical saturation loss.
Materials and Instruments
Material: plant tissue. Move The basic procedure for determining the water content of plant tissue can be divided into the following steps: 1. Cut the plant tissue and quickly place it into an aluminum box of known weight and weigh the fresh weight ( Wf ). 2. 2. put the plant tissues together with the aluminum box into an oven which has been heated up to 105 ℃, kill the green for 15 min, and then bake at 80 ℃ until the constant weight, and weigh the dry weight ( Wd ). 3. determine the relative water content, and then weigh the dry weight ( Wd ). 3. Determine the relative water content, weigh the fresh weight, the sample will be immersed in steaming crane water or wrapped in moisture-absorbing wet gauze 6~8 h, remove the absorbent paper to wipe dry the sample surface water, weighing; and then immerse the sample in steaming water for 1 h, remove the sample, dry it, weigh it until the sample saturated weight approximation, i.e., get the saturated fresh weight of the sample ( Wt ); if known in advance to reach the time used in the saturation of water, it can be weighed once If the time taken to reach moisture saturation is known in advance, the saturated fresh weight can be measured in one weighing, and then dried and weighed out the dry weight ( Wd ). 4. 4. Wf, Wd, Wt values obtained by substituting into the formula (1-1), (1-2), (1-3), (1-4) or (1-5), the sample moisture content, relative moisture content and moisture saturation loss. Caveat 1. When drying the plant material, the killing time should not be too long. 2. drying at 80 ℃ for 1 day, weighing, and then continue to dry at 80 ℃, then weighing until constant weight. For more product details, please visit Aladdin Scientific website.
Equipment:
① Balance (sensitivity 0.1 mg)
② Oven
③ Scissors
④ 100 mL beaker
⑤ Aluminum box
⑥ Absorbent paper
