Mouse ex vivo cardiac perfusion is a commonly used physiologic experiment to assess physiologic function and drug effects in the mouse heart. The experiment simulates the in vivo environment by removing the mouse heart from the body and perfusing it with saline in order to assess the systolic and diastolic functions of the heart.
Principle
The principle of ex vivo cardiac perfusion is based on the physiological function of the heart and blood circulation. In the experiment, the mouse heart is removed from the body and perfused retrogradely through the great vessels, i.e., the perfusate is perfused from the aorta into the coronary circulation. During the perfusion process, the heart's response to different drugs and stimuli can be evaluated by adjusting the parameters of the perfusate composition and flow rate.
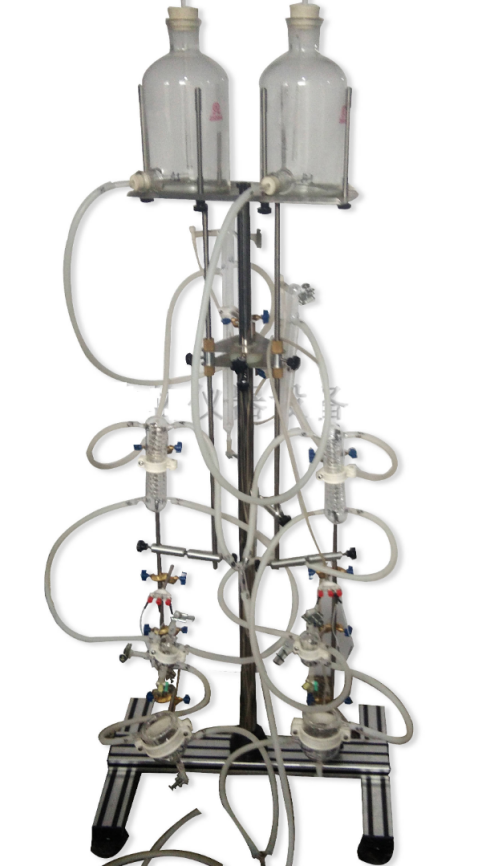

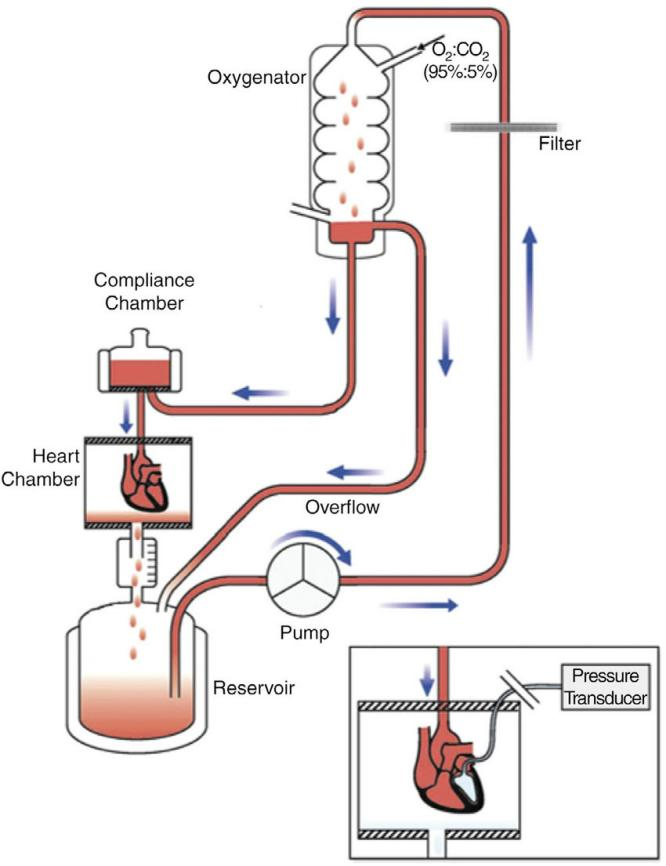
Operation method
Mouse isolated heart perfusion technique
Principle
The principle of ex vivo cardiac perfusion is based on the physiological function of the heart and blood circulation. In the experiment, the mouse heart is removed from the body and perfused retrogradely through the great vessels, i.e., the perfusate is perfused from the aorta into the coronary circulation. During the perfusion process, the heart's response to different drugs and stimuli can be evaluated by adjusting the parameters of the perfusate composition and flow rate.
Materials and Instruments
Set of surgical instruments, syringes, needles, string, murine operating table, perfusion fluid bottles, cardiac Langendorff method perfusion set, thermostatic circulator, pulleys, beakers, measuring cylinders, corrected Roche's solution, 1:10,000 epinephrine, 1:10,000 acetylcholine. ECG recorder, recording forms. Move 1、Preparation Prepare the experimental equipment, including the isolated heart perfusion device, ECG recorder and so on. 2.Extraction of heart Mice were injected intraperitoneally with heparin (0.4 ml/100 g) for anticoagulation. 30 min later, mice were injected intraperitoneally with 20% ethyl carbamate (3 ml/kg), and after anesthesia, mice were fixed in supine position on the operating table. The mice were anesthetized and fixed on the surgical table in a supine position. The skin was quickly cut along the middle of the anterior chest wall, the chest cavity was opened, the heart was gently lifted up, and the vena cava, aorta, and the tissues around the heart were carefully cut, and the heart was quickly removed together with a section of the aorta. During the procedure, care should be taken not to damage the heart, and the root of the aorta should be left at a length of 0.5-1 cm for cannulation. Immediately after the heart is removed, it is placed in pre-prepared oxygenated cold cathartic fluid (around 4 ℃), and the ventricle is pressed gently with a finger to facilitate the discharge of the blood remaining in the heart and to prevent the formation of blood clots. After the heart stops beating, quickly cut the pericardium and cut away the tissues around the heart (including lung tissues, trachea, and other tissues attached to the heart), recognize the anatomical positions of the aorta, vena cava, and pulmonary artery, and wear a cotton thread at the root of the aorta for backup. 3. Perfusion of the heart Put the aorta into the mouth of the cardiac cannula, use cotton thread to tie the aorta and cardiac cannula together and fixed. The cannula should not be too deep into the aorta, so as not to damage the aortic valve and block the opening of the coronary artery, affecting the coronary vascular perfusion. After the heart is perfused by the oxygenated Winculo's solution, the heart can start to beat again within 1 min, but the heart rate is slow at first, and there is often arrhythmia, and then it gradually becomes faster and the heart rhythm gradually returns to normal and stable, and it can be maintained for several hours. 4、Record Set the parameters of the instrument, during the cardiac perfusion process, through the ECG recorder to monitor the heart's electrical signal changes, in order to assess the systolic and diastolic function of the heart. Adjust and fix the insulation perfusion tank so that the insulation perfusion tank covers the heart. The perfusate enters the coronary vessels and then goes to the right atrium and drips into the double-layer perfusion trough via the vena cava and pulmonary artery, and flows out through the funnel-shaped opening at the bottom of the trough, and the effluent collected with a measuring cylinder for a certain period of time is the coronary flow rate. During perfusion, different drugs or stimulants (epinephrine solution/acetylcholine solution) can be added to assess the heart's response to them. 5. Analysis The results of the experiments were analyzed to assess the physiological function of the mouse heart and the drug effects. Caveat 1. Before conducting the experiment, the experimental equipment needs to be sufficiently cleaned and sterilized to avoid any influence on the experimental results. 2. During the experiments, attention should be paid to the health status of the mice and the integrity of the heart, and abnormalities should be recorded and dealt with in a timely manner. 3. During the experiments, attention should be paid to controlling the consistency of the experimental conditions, such as the composition of the perfusate and flow rate and other parameters, in order to ensure the comparability and reproducibility of the experimental results. 4. when performing ECG recording, attention should be paid to the stability and accuracy of the signal, and filtering and amplification should be performed as needed. 5. in the course of the experiment, attention should be paid to the conditions of the environment, such as temperature and humidity, to ensure the temperature of the perfusate and the normal function of the heart. 6. when adding drugs or stimulants, attention should be paid to the control of dosage and concentration in order to avoid excessive stimulation or damage to the heart. 7. When analyzing the experimental results, care should be taken to consider a variety of factors in the experimental process, such as mouse breed, age, sex, diet and environment, etc., in order to fully assess the reliability and practicality of the experimental results. 8. Isolated mouse cardiac perfusion is a complex experiment that requires a certain degree of specialized knowledge and skills, as well as adequate experimental design and control to ensure the reproducibility and accuracy of the experiment. For more product details, please visit Aladdin Scientific website.