Soluble sugar is mostly some sugar with sweet flavor, such as glucose, fructose, sucrose, maltose and so on. Soluble sugar content is an important indicator of fruit quality and increases during fruit ripening. Soluble sugars are also one of the osmoregulatory substances in plant cells, and their content increases in plant tissues under drought conditions. Determination of soluble sugar content can be used to analyze the quality of fruits and understand the physiological condition of plants. The purpose of this experiment is to learn the principle and method of the onion-ketone colorimetric method for the determination of soluble sugar content.
Principle
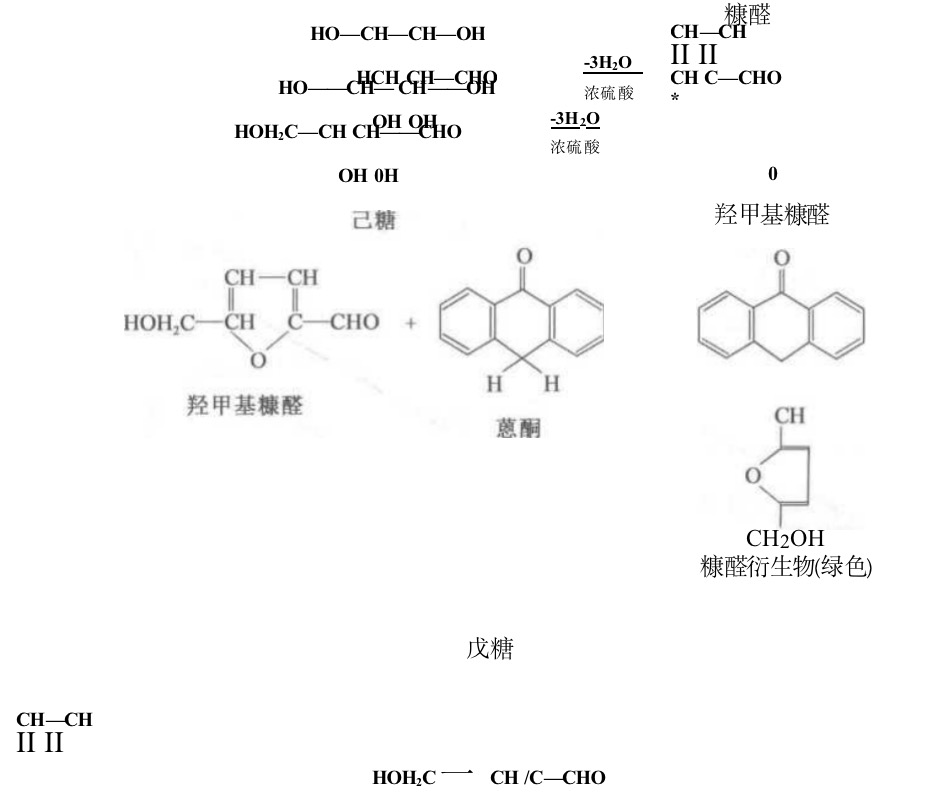
The basic principle of the determination of soluble sugar content in plant tissues is that sugar (sugar) under the action of concentrated sulfuric acid, can be generated by dehydration reaction furfural or hydroxymethylfurfural, generated furfural or hydroxymethylfurfural and onion ketone dehydration condensation, the formation of furfural derivatives, blue-green color, and the absorption peak of 625 nmo within a certain range, the color of the color of the depth of the sugar content is proportional to the amount of sugar, so it can be used for the quantitative determination of sugar.
Operation method
Determination of soluble sugar content in plant tissues
Principle
The basic principle of the determination of soluble sugar content in plant tissues is that sugar (sugar) under the action of concentrated sulfuric acid, can be generated by dehydration reaction furfural or hydroxymethylfurfural, generated furfural or hydroxymethylfurfural and onion ketone dehydration condensation, the formation of furfural derivatives, blue-green color, and the absorption peak of 625 nmo within a certain range, the color of the color of the depth of the sugar content is proportional to the amount of sugar, so it can be used for the quantitative determination of sugar.
Materials and Instruments
Materials: various plant tissues such as roots, stems, leaves, fruits, seeds, etc. Move The basic procedure for the determination of soluble sugar content in plant tissues can be divided into the following steps:1. Preparation of standard curve: Take 7 large test tubes, add reagents according to Table 52-1, shake well immediately, cover with lid, boil in boiling water bath for 10 min, remove and cool down to room temperature, adjust the zero with 0 tube, and then compare the color at the wavelength of 625 nm. Take the standard glucose content as the horizontal coordinate and the absorbance value as the vertical coordinate to draw the standard curve.Table 52-1 Standard Curve Preparation and Addition Table Caveat 1. The residue left from the extraction of soluble sugars is dried in an oven at 80°C and can be used for the determination of starch and cellulose. 2. Since the color intensity of the reaction of the onion-ketone reagent with sugar varies with time, the color must be measured at the same time immediately after the reaction. For more product details, please visit Aladdin Scientific website.
Equipment: spectrophotometer, balance, water bath, centrifuge or funnel, stoppered graduated test tubes, volumetric flasks, pipettes, etc.
Reagents:
①80% ethanol
②100μg-mL
②100μg-mL -1
Standard glucose solution: accurately weigh 100 mg of glucose dried to constant weight, dissolve it in 80% ethanol and then dilute it to 1,000 mL.
③Anion Ketone Reagent: Weigh 0.1 g of onion ketone and dissolve it in 100 mL of sulfuric acid solution (76 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid with a relative density of 1.84 was diluted to 100 mL with distilled water), store it in a brown bottle, and prepare it for use on the same day.
2. Sample Extraction: Dry and crush the plant tissues, weigh 50~250 mg accurately, put it into a stoppered graduated test tube, add 80% ethanol 10~15 mL, and extract for 30 min in a boiling water bath; centrifuge and collect the supernatant, and then add 80% ethanol 10~15 mL to the residue to repeat the extraction for two times, and then merge the supernatant. For green tissue, add a small amount of activated charcoal to the extract at 70 笆, decolorize, filter and dilute to 50 mL for measurement. For fresh samples, weigh 0.5-1 g, add a little quartz sand to make a homogenous pulp, and then add the residue together with evaporated water to 100 mL, and then extract the sample for 30-60 min at room temperature with frequent shaking, then centrifuged or filtered, and then discard the residue, and then dilute it appropriately before measurement.3. Determination of samples: Pipette 1 mL of extract into a large test tube, add 5 mL of onion and ketone reagent, shake well, use the same method as above, colorimetry at 625 nm, record the absorbance value, and then find out the content of soluble sugar in the extract from the standard curve.4 . Calculation of results:Soluble sugar content = I ching><1. %.Where: I-sucrose concentration from the standard curve, 卩 g.mL-1 ;V-Total volume of sample, mL;W-sample weight, mg. Reagent Tube No. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Standard glucose solution/mL 0 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 Evaporated pomegranate water/mL 1.0 0.9 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Sucrose concentration/(ptg・mL'1 ) 0 10 20 40 60 80 100 Onion ketone reagent/mL 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
